 00:04:00
00:04:00
Longboard physics
A few (surprising?) thoughts on how the wheels on a longboard or skateboard actually move.
More details | Watch now 00:07:00
00:07:00
The Longboard – speedometer
Jonathan describes his adventures with a longboard and some different methods of making a speedometer for it.
More details | Watch now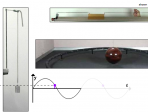 00:09:00
00:09:00
Oscillations
Inertia and restoring forces can, with low friction or damping, lead to oscillations and resonance. We analyse the mechanics of vibrations.
More details | Watch now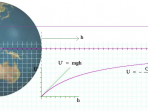 00:12:00
00:12:00
Gravity
The inverse square law explains planetary motion - and apples falling. Newton's law, measuring G, calculating orbits.
More details | Watch now 00:10:00
00:10:00
Rotation
Torques produce angular acceleration, moment of inertia 'resists' it. Rotational kinetic energy and angular momentum.
More details | Watch now 00:10:00
00:10:00
Momentum
p=mv. If external forces are zero, momentum is conserved. In collisions, energy may be conserved (elastic) or not (inelastic).
More details | Watch now 00:08:00
00:08:00
Centre of mass
In finite objects, the total external force equals the total mass times the acceleration of a point called the centre of mass.
More details | Watch now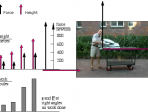 00:10:00
00:10:00
Energy and power
The total work done on an object equals the increase in its kinetic energy. For conservative forces, we can define potential energy.
More details | Watch now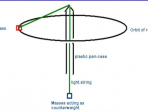 00:06:00
00:06:00
Centripetal force – how do we measure it?
A short video showing a simple classroom method of checking the way in which this force is related to mass, speed and radius.
More details | Watch now 00:14:00
00:14:00
Going round in circles – how do we do it?
A presentation showing both the ideas about centripetal force and a simple classroom method of checking the way in which this force is related to mass, speed and radius.
More details | Watch now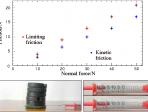 00:10:00
00:10:00
Weight and contact forces
Carefully distinguish mass and weight. Hooke's law quantifies deformation. Contact forces have normal and frictional components.
More details | Watch now 00:29:00
00:29:00
Life in Space
Helen Sharman, the UK's first astronaut, gives a vibrant account of her personal experience of life in space using models and film to illustrate the key scientific concepts involved in spaceflight. Among other things she discusses the way Newton's Th....
More details | Watch now 00:10:00
00:10:00
Newton’s laws of motion
F=ma (laws 1&2). Forces come in pairs that add to zero (3). Newton's laws apply in inertial frames of reference. Some common approximations made in applying them.
More details | Watch now 00:08:00
00:08:00
Simple harmonic motion
In simple harmonic motion, displacement, velocity and acceleration vary sinusoidally with time, but with different phases.
More details | Watch now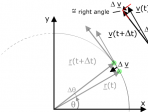 00:08:00
00:08:00
Circular motion
Uniform circular motion: angular displacement and velocity are introduced and centripetal acceleration is determined.
More details | Watch now 00:09:00
00:09:00
Projectile motion
Motion with uniform acceleration, such as in a uniform gravitational (or electric) field is projectile motion, analysed here with examples.
More details | Watch now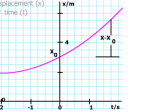 00:06:00
00:06:00
Motion with constant acceleration (kinematics)
Kinematics quantifies motion without explaining the causes of it. Here we study accelerations that are zero, positive or negative.
More details | Watch now 00:11:00
00:11:00
Crater Formation in Sand
A description and demonstration of the way in which craters formed by dropping objects into sand can be linked to some elementary physics
More details | Watch now 00:37:00
00:37:00
A Quantum Gas
The quantum gas is an extreme state of an ensemble of atoms when their de Broglie wave length is of the same length as the size of the container. The ways of achieving this state are described and also how its temperature is defined.
More details | Watch nowItems per page:


